ML Copilot executes leakage-aware workflows across genomics, proteomics, and hematology data—turning task cards into calibrated models, decision-curve analysis, and citable manifests without bespoke scripting.
Handle missing values, encoding, scaling, and feature engineering
Recommends models based on problem type and dataset
Generates metrics, visualizations, and ready-to-share reports
The copilot replicated six task cards from our manuscript—spanning TCGA, CPTAC, and clinical CBC datasets— with deterministic seeding, leakage checks, and calibrated outputs. Highlights from the four flagship case studies:
RNA-seq clustering and supervised refinement discovered a 12-gene signature that stratified TCGA survival and generalized to CPTAC validation.
Harmonized expression matrices enabled cross-cohort subtype prediction with disciplined ComBat ablations and probability calibration.
Parallel RNA vs proteome pipelines quantified hormone receptor status with calibration curves and net-benefit analysis for ER/PR/HER2.
Routine labs plus derived Mentzer-style indices delivered interpretable triage with SHAP explanations for physicians.
User provides natural language instructions for ML tasks
GPT-4o/Gemini interprets request and generates Python code
Code interpreter safely executes generated Python code
Outputs, visualizations, and files are returned to user
Each workflow step is an event with explicit inputs, schema validation, deterministic seeds, and rollback protection. The copilot records prompts, generated code, package versions, SHAP/DCA assets, and final manifests for exact reproduction.
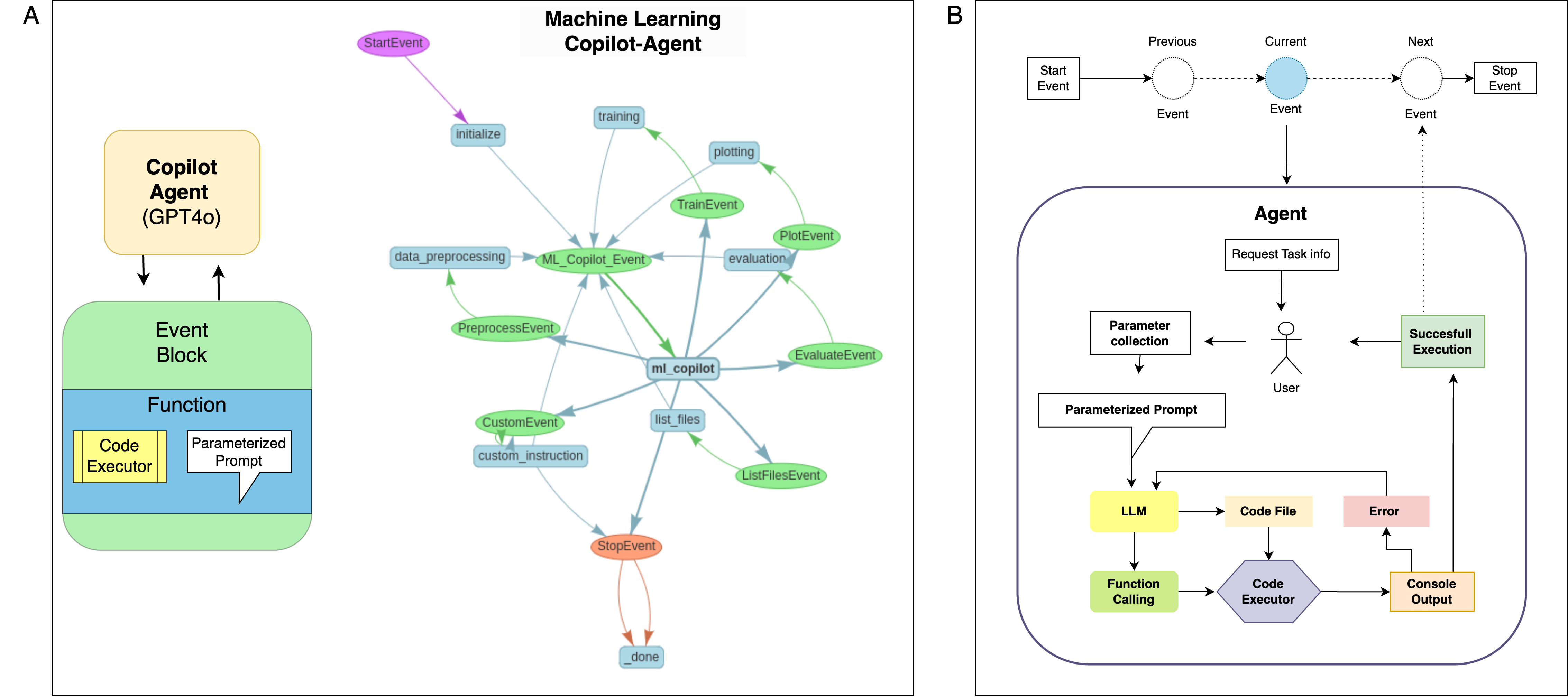
The manuscript’s system diagram shows the GPT-4o/Gemini planner orchestrating sandboxed Python execution via LlamaIndex events with provenance captured at each hop.
Direct exports from the manuscript highlight what the copilot produced—Kaplan-Meier survival plots, subtype transfer precision-recall curves, receptor-status comparisons, and SHAP-based interpretability. Each figure is reproducible from the task cards shipped with ML Copilot.
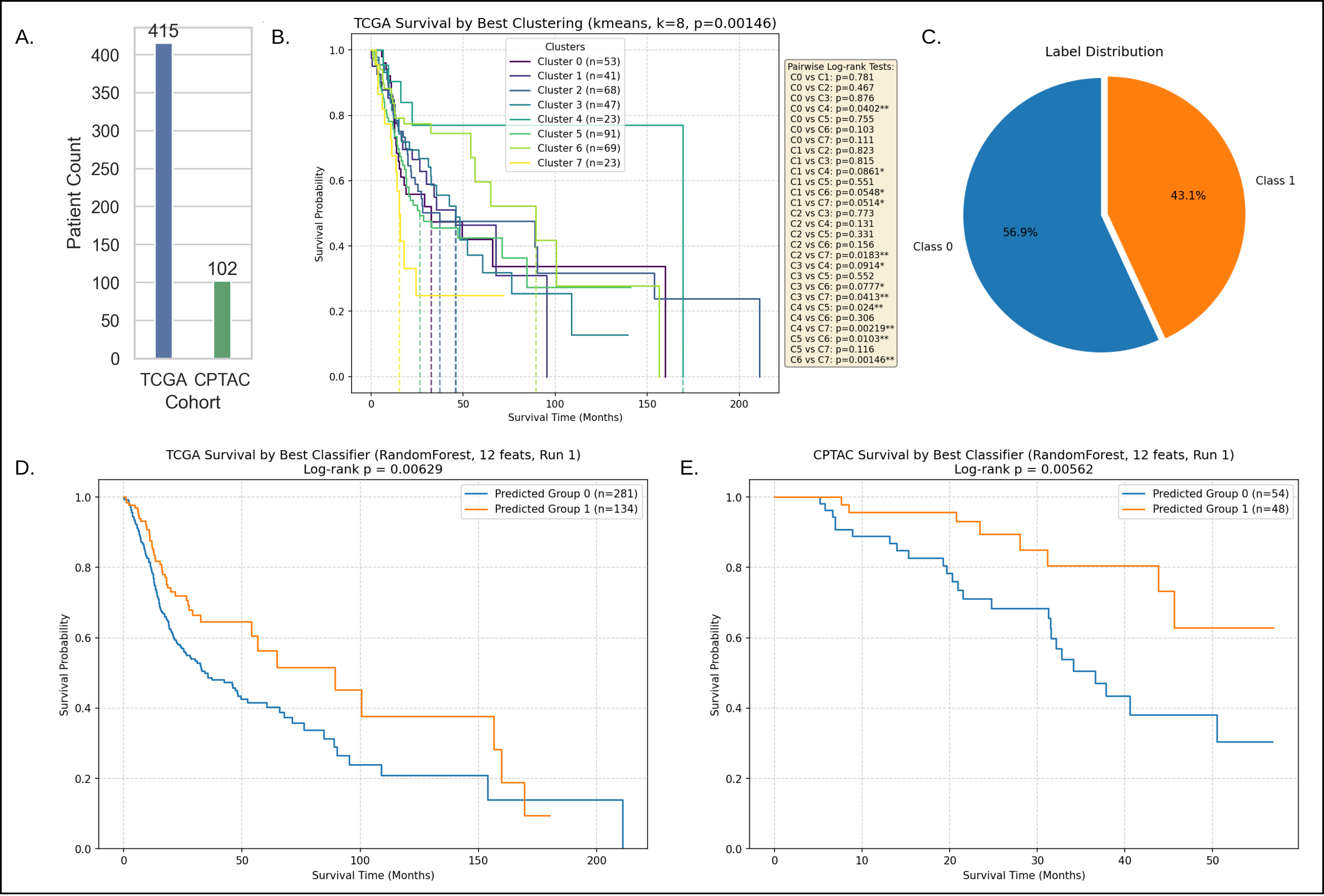
Case Study 1: Survival stratification for HNSCC with TCGA discovery and CPTAC validation showing the 12-gene classifier’s log-rank separation.
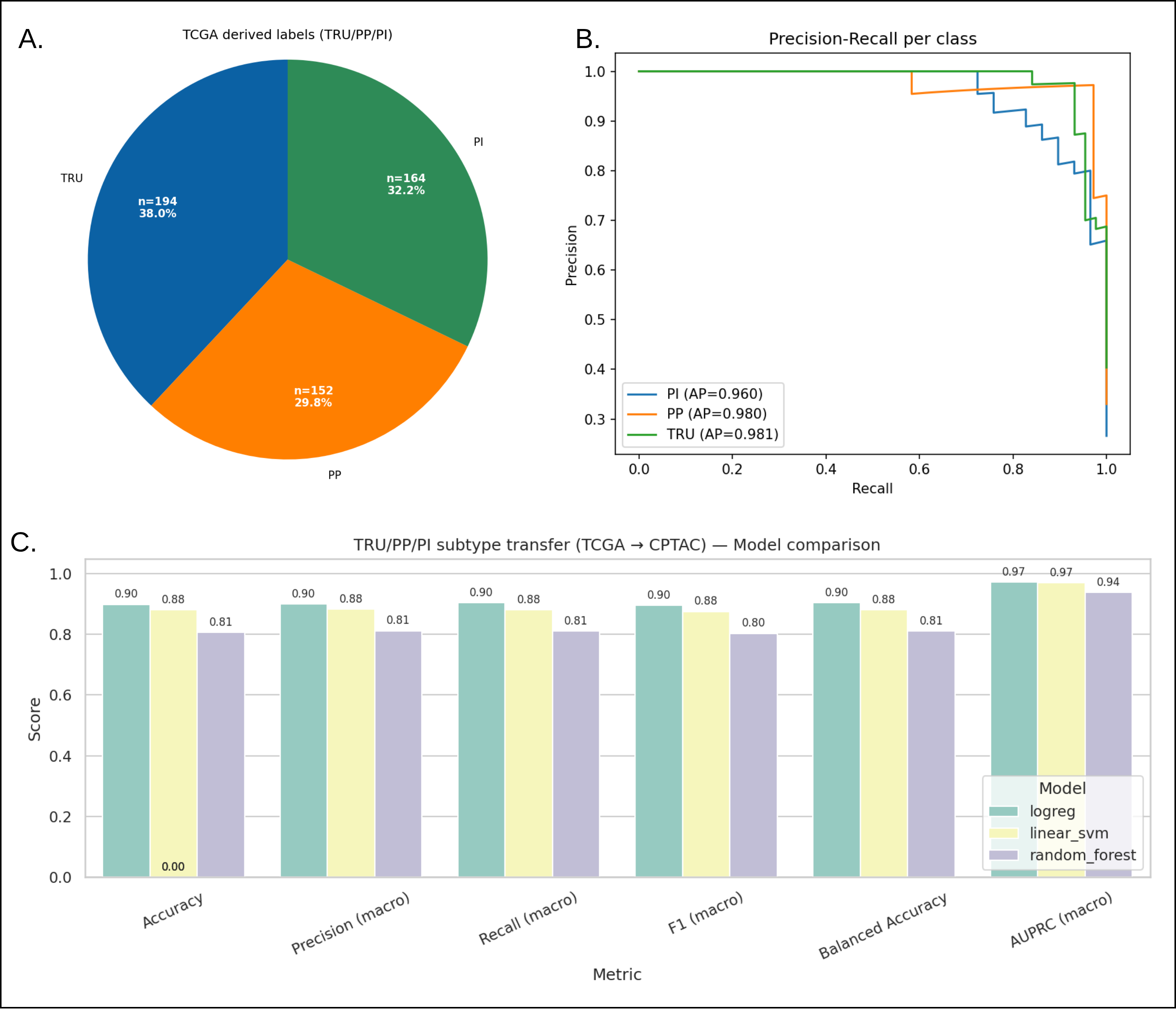
Case Study 2: Cross-cohort LUAD TRU/PP/PI transfer with per-class precision-recall curves and balanced accuracy summaries for linear vs. tree-based models.
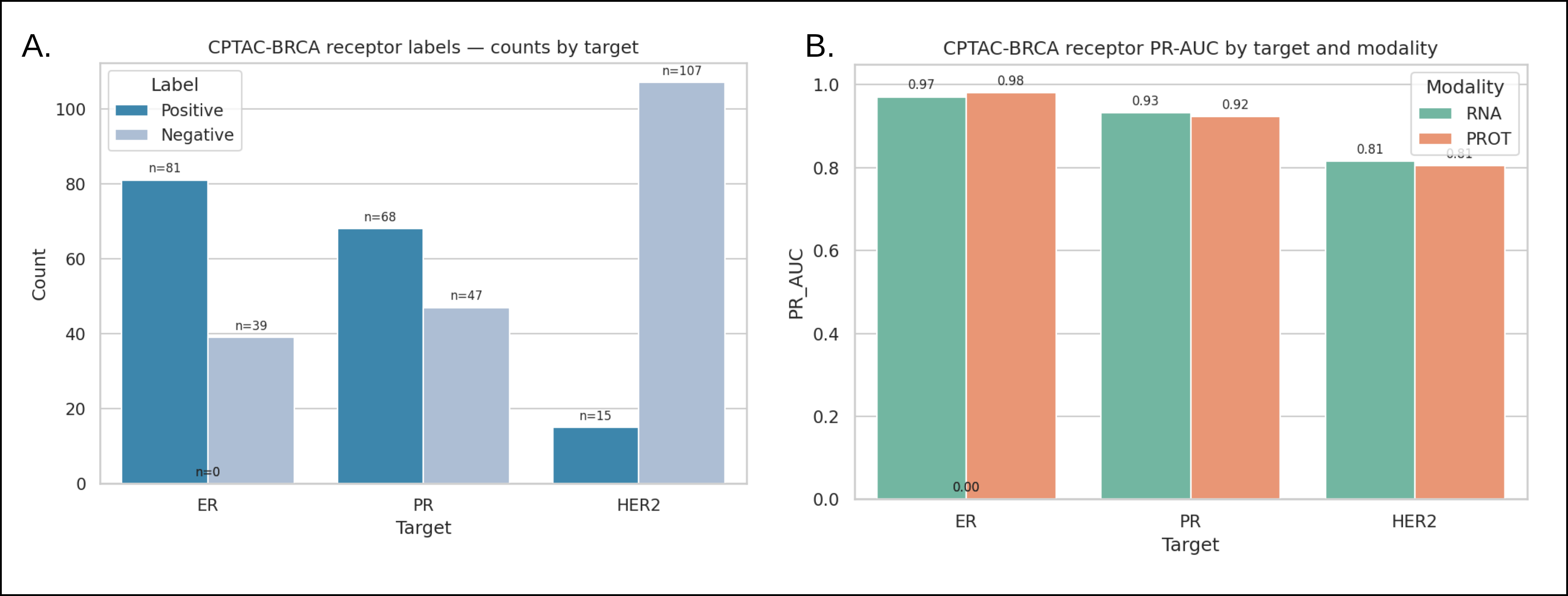
Case Study 3: RNA vs. proteome comparison for ER/PR/HER2 receptor status including label distributions and modality-specific PR-AUC.
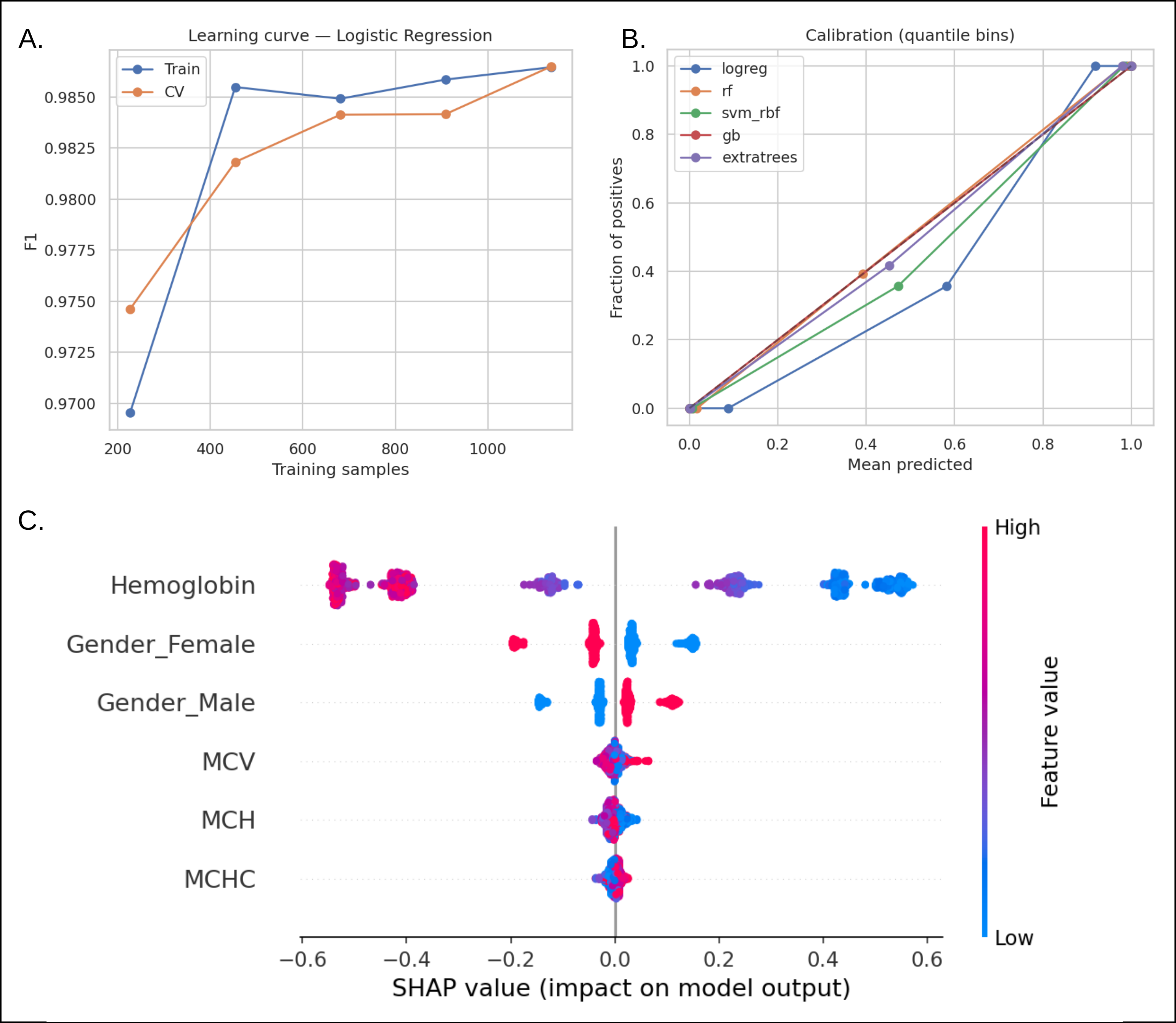
Case Study 4: CBC-based anemia classification with learning curves, calibration overlays, and SHAP feature importances that mirror hematology heuristics.
list files
Show files in current directory
preprocess data.csv target=outcome
Clean and prepare your dataset
train model=random_forest
Train a machine learning model
plot confusion_matrix
Visualize model performance
document
Generate analysis report
Our preprint "ML Copilot: An LLM-Powered Agent for Orchestrating Complex Machine Learning Workflows" is currently under peer review at the Journal of Engineering Artificial Intelligence.
Partner with HFR on pilots, research collaborations, or enterprise integrations across healthcare and biosciences.